Omega-3-, Omega-6- und Omega-9-Fettsäuren sind essenzielle Bestandteile einer ausgewogenen Ernährung. Diese Fette spielen eine zentrale Rolle für die Herzgesundheit, die Gehirnfunktion und das allgemeine Wohlbefinden. Es ist jedoch entscheidend, ihre Unterschiede, Vorteile und das ideale Verhältnis der Aufnahme zu verstehen, um ihr Potenzial optimal zu nutzen. Dieser Guide bietet einen tiefgehenden Einblick in diese Fettsäuren, ihre Quellen und praktische Tipps, wie man sie im Alltag ausbalanciert.
Was sind Omega-Fettsäuren?
Omega-3-, Omega-6- und Omega-9-Fettsäuren sind Arten von ungesättigten Fetten. Omega-3 und Omega-6 sind essenzielle Fette, das heißt, der Körper kann sie nicht selbst herstellen und muss sie über die Nahrung aufnehmen. Omega-9 ist zwar nicht essenziell, bietet aber zusätzliche gesundheitliche Vorteile, wenn es konsumiert wird.
Omega-3-Fettsäuren
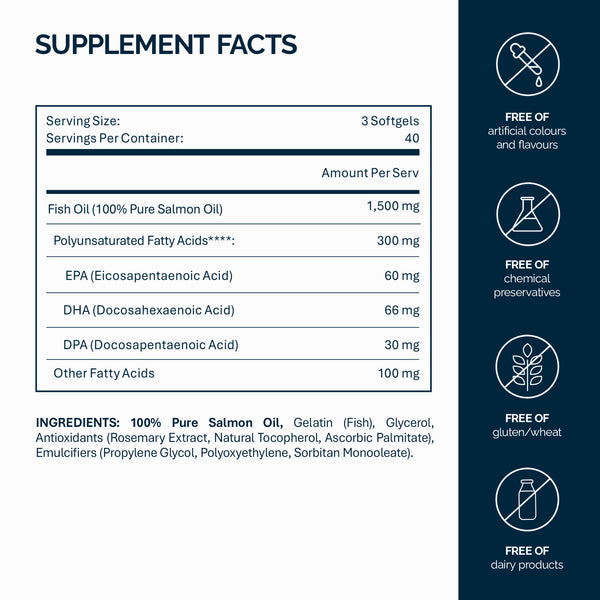
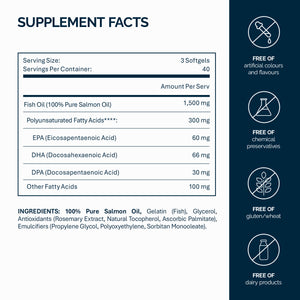
Omega-3s sind mehrfach ungesättigte Fette, die entscheidend sind, um Entzündungen zu reduzieren, die Gehirngesundheit zu unterstützen und das Herz zu schützen. Wichtige Typen sind Eicosapentaensäure (EPA), Docosahexaensäure (DHA) und Alpha-Linolensäure (ALA). EPA und DHA kommen hauptsächlich in fettem Fisch vor, während ALA in pflanzlichen Quellen wie Leinsamen und Walnüssen enthalten ist.
Omega-6-Fettsäuren
Omega-6s sind ebenfalls mehrfach ungesättigte Fette. Sie spielen eine Rolle bei der Gehirnfunktion, der Hautgesundheit und der Regulierung von Entzündungen. Die wichtigste Omega-6-Fettsäure ist Linolsäure, die in pflanzlichen Ölen, Nüssen und Samen vorkommt.
Omega-9-Fettsäuren
Omega-9s sind einfach ungesättigte Fette, die häufig in Olivenöl, Avocados und Nüssen zu finden sind. Diese Fette helfen, den schlechten Cholesterinspiegel zu senken und die Herzgesundheit zu verbessern.
Gesundheitsvorteile von Omega-3-6-9
Vorteile von Omega-3
- Herzgesundheit: Omega-3s senken die Triglyzeride, reduzieren den Blutdruck und verhindern die Bildung von Plaque in den Arterien.
- Gehirnfunktion: DHA ist essenziell für die Gehirnentwicklung und die kognitive Leistungsfähigkeit.
- Entzündungshemmende Wirkung: EPA hilft, chronische Entzündungen zu bekämpfen und so das Risiko für Arthritis und andere entzündliche Erkrankungen zu senken.
Vorteile von Omega-6
- Haut- und Haargesundheit: Linolsäure unterstützt die Feuchtigkeit und Elastizität der Haut.
- Gehirnentwicklung: Omega-6s spielen eine Rolle bei der Gehirnentwicklung während der Schwangerschaft und in der frühen Kindheit.
Vorteile von Omega-9
- Herzgesundheit: Omega-9s können helfen, den LDL-Cholesterinspiegel zu senken und das HDL-Cholesterin zu verbessern.
- Entzündungshemmende Wirkung: Omega-9s unterstützen die allgemeine Reduktion von Entzündungen.
Das Gleichgewicht der Omega-Fettsäuren
Das richtige Verhältnis zwischen Omega-3- und Omega-6-Fettsäuren zu halten, ist entscheidend. Eine typische westliche Ernährung enthält oft zu viele Omega-6s und zu wenig Omega-3s, was zu vermehrten Entzündungen und damit verbundenen Gesundheitsrisiken führen kann.
Optimale Verhältnisse
Das empfohlene Verhältnis von Omega-6 zu Omega-3 liegt bei etwa 4:1 oder niedriger. Um dieses Verhältnis zu erreichen, sollte die Aufnahme von Omega-3 erhöht und der Konsum von Omega-6 moderat gehalten werden.
Praktische Tipps
- Baue fettreichen Fisch wie Lachs und Makrele mindestens zweimal pro Woche in deinen Speiseplan ein.
- Verwende Olivenöl oder Avocadoöl anstelle von pflanzlichen Ölen mit hohem Omega-6-Gehalt.
- Füge omega-3-reiche Lebensmittel wie Leinsamen, Chiasamen und Walnüsse zu deinen Mahlzeiten hinzu.
Supplementierung mit Omega-3-6-9
Omega-3-6-9-Supplements bieten eine bequeme Möglichkeit, eine ausgewogene Aufnahme sicherzustellen. Es ist jedoch wichtig, hochwertige Produkte zu wählen, die den Fokus auf Omega-3 legen, da die meisten Ernährungsweisen bereits ausreichend Omega-6 und Omega-9 liefern.
Worauf du bei der Auswahl eines Supplements achten solltest
- Achte auf Supplements mit einem höheren Anteil an Omega-3 im Vergleich zu Omega-6.
- Stelle sicher, dass das Produkt von unabhängigen Dritten auf Reinheit und Wirksamkeit getestet wurde.
- Wähle Supplements, die EPA und DHA enthalten, um den maximalen gesundheitlichen Nutzen zu erzielen.
Mögliche Risiken und Nebenwirkungen
Obwohl Omega-3-6-9-Fettsäuren zahlreiche gesundheitliche Vorteile bieten, kann eine übermäßige Aufnahme zu Nebenwirkungen wie Magen-Darm-Beschwerden und Blutverdünnung führen. Es ist wichtig, die empfohlenen Dosierungen einzuhalten und bei Medikamenteneinnahme ärztlichen Rat einzuholen.
Fazit
Omega-3-6-9-Fettsäuren sind essenziell für die Erhaltung der allgemeinen Gesundheit und des Wohlbefindens. Wenn du ihre individuellen Rollen, Vorteile und das richtige Gleichgewicht verstehst, kannst du deine Ernährung und Supplementierung optimieren, um bessere Gesundheitsergebnisse zu erzielen. Achte darauf, Omega-3 zu priorisieren, Omega-6 in Maßen zu konsumieren und Omega-9 aus gesunden Quellen einzubauen, um einen ausgewogenen und nährstoffreichen Lifestyle zu leben.
Quellen
- Calder, P.C. (2010). Omega-3 fatty acids and inflammatory processes. Biochimica et Biophysica Acta, 1851(4), 469-484. DOI: 10.1016/j.bbalip.2015.11.007.
- Fujimoto, W.Y., et al. (2013). Skin hydration and omega-6. Journal of Dermatological Science, 69(3), 234-240. DOI: 10.1016/j.jdermsci.2013.09.003.
- Innis, S.M. (2008). Dietary omega-3 fatty acids in brain development. American Journal of Clinical Nutrition, 87(2), 529S-532S. DOI: 10.1093/ajcn/87.2.529S.
- Jones, P.J., et al. (2010). Omega-9 fatty acids in heart health. Journal of Nutrition, 140(7), 1278-1283. DOI: 10.3945/jn.110.120113.
- Simopoulos, A.P. (2011). Importance of omega-3 and omega-6 in health. Journal of Nutrition and Metabolism, 18(3), 153-157. DOI: 10.1155/2011/327965.