DHA (docosahexaenoic acid) is a superstar of the omega-3 fatty acid family, renowned for its role in brain health and development. If you are an expecting mum or a health-conscious woman, you have likely seen DHA mentioned on prenatal vitamins, fish oil bottles, or heard it touted for baby’s development. Here, we break down what DHA is, its benefits for general health and pregnancy, how it stacks up against its omega-3 cousin EPA, and how to choose the right DHA supplement (including vegan options). Let us dive into the world of DHA and why it is worth the hype – no fishy business about it.
What is DHA?
DHA is an omega-3 fatty acid – essentially a type of healthy polyunsaturated fat. Along with EPA (eicosapentaenoic acid) and ALA (alpha-linolenic acid), it forms the trio of major omega-3s. Unlike ALA (found in flaxseed and walnuts), DHA and EPA are the long-chain omega-3s mostly found in marine sources. Our bodies can only make minimal DHA on their own, so we rely on dietary intake or supplements. DHA is a building block of our brain, eyes and nerves – in fact, it is the most abundant omega-3 in the human brain and retina. (Fun fact: DHA makes up about 97% of the omega-3 content in the brain, underscoring its importance for cognitive function.)
Because it is so critical to cell membranes in the brain and eyes, DHA is often nicknamed “brain food”. It is not a vitamin or a drug, but a nutrient our body truly needs for optimal development and health. Do not confuse it with “DHEA” (a hormone supplement) or DHA in tanning products (which is a completely different ingredient) – the DHA we are discussing is all about omega-3. In summary, DHA is a key omega-3 fat that keeps your mind sharp and your eyes bright, and it is especially vital during certain life stages like pregnancy.
Key benefits of DHA for health
DHA punches well above its weight in supporting various aspects of health. Whether you get it from oily fish, fortified foods, or a supplement, here are some of the science-backed benefits of DHA (often in tandem with EPA, its fellow omega-3):
- Heart health support: Omega-3s like DHA help maintain a healthy heart by promoting normal blood pressure and cholesterol levels. They contribute to a lower risk of heart disease by reducing triglycerides and supporting good circulation.
- Brain and cognitive function: DHA is literally brain fuel – it supports memory, learning, and overall cognitive performance. Adequate DHA has been linked to better retention and may even help slow cognitive decline as we age. Keeping DHA levels up is like giving your brain’s hardware the proper upgrades.
- Eye health and vision: DHA is a major structural fat in the retina of the eye. It helps keep vision sharp and supports eye development and function. This is why DHA is often recommended for children’s visual development and why it is included in many infant formulas.
- Anti-inflammatory effects: Together with EPA, DHA has anti-inflammatory properties. Omega-3s can balance the body’s inflammatory response, which may alleviate joint pain and support mobility. For anyone dealing with stiff joints or post-workout soreness, this is a notable perk.
- Healthy skin and hair: Getting enough omega-3s can nourish your skin from within, helping maintain its elasticity and moisture. Some people find their skin has more of a healthy glow and their hair may appear shinier when they include DHA/EPA in their diet – think of it as beauty from the inside out.
- Immune function: DHA, along with EPA, supports a healthy immune system. It aids in regulating immune responses, helping the body strike the right balance in fighting infections without excessive inflammation.
In short, DHA is a multitasking nutrient that benefits your heart, mind, eyesight, joints, and even appearance. No wonder doctors often recommend getting enough omega-3s for overall wellness.
(Note: Many of these benefits are observed when DHA and EPA work together, as they naturally do in fish oil. Each fatty acid has some unique strengths – for instance, EPA is highlighted for cardiovascular and mood benefits, while DHA shines for brain and eye health – but both are valuable for well-being.)
DHA in pregnancy: support for expecting mums
If you are pregnant or planning to be, DHA is about to become your new best friend. Pregnancy is a time when DHA needs are at their highest, because you are not just maintaining your own health – you are also building your baby’s brain and body. DHA is critical for fetal brain and eye development. In the third trimester, a baby’s brain growth surges, and DHA is a major component of those brand-new brain cells and retinal tissue.
Research shows that getting enough DHA during pregnancy can have lasting positive effects on the child’s development. Babies whose mums had sufficient DHA intake tend to show better cognitive function, attention, and visual acuity in infancy and early childhood. Put simply, DHA is helping to lay the foundation for your little one’s learning, memory, problem-solving skills and eyesight. It is like giving your baby a head-start on a healthy brain and keen eyes.
DHA is not just for the baby’s benefit – it supports mum’s health too. Adequate DHA and EPA in pregnancy are linked to a healthy full-term pregnancy (including supporting a healthy birth weight and gestational length). In fact, some studies suggest that omega-3 supplementation, particularly DHA, can reduce the risk of premature birth, which is a significant benefit for both baby and mother. Additionally, omega-3s contribute to maternal well-being: women who maintain good DHA/EPA levels may experience better mood balance, potentially lowering the risk of postpartum depression. Pregnancy and early motherhood can be mentally challenging, and DHA is one nutrient that may help support a positive mood during this time.
Because many women start off pregnancy with low omega-3 stores (and the developing baby will draw on the mother’s DHA supply), health experts strongly recommend that expecting and breastfeeding women get enough DHA. How much DHA do you need in pregnancy? Doctors and nutritionists often advise at least 200–300 mg of DHA per day for pregnant and lactating women. This is the amount thought to optimally support fetal development. For example, the International Society for the Study of Fatty Acids and Lipids recommends a minimum of about 300 mg DHA daily in pregnancy. If your prenatal vitamin does not contain DHA, don’t worry: you can take a separate DHA supplement alongside your prenatal vitamins. In fact, pairing DHA with your regular prenatal (which typically covers folic acid, iron, vitamin D, etc.) is a smart move to cover all bases for you and your baby.
It is worth noting that pregnant women are often advised to eat 1–2 portions of oily fish per week (like salmon or sardines) to obtain DHA naturally. However, due to concerns about mercury and other contaminants in fish, there are limits on fish intake during pregnancy. This is where a purified DHA supplement can shine – it provides the benefits of fish oil without the risk of pollutants. High-quality fish oil supplements undergo filtration to remove mercury and other toxins, making them safe for pregnancy. Always choose a reputable brand that tests for purity, especially if you are expecting.
In summary, DHA is the omega-3 you definitely want on your team during pregnancy. It supports your baby’s brain, eye, and immune development, contributes to a healthy pregnancy outcome, and even helps mum recover and feel her best after birth. Think of DHA as a crucial prenatal nutrient – just like folic acid – for nurturing a healthy mum and baby.
DHA vs EPA: what is the difference?
You will almost always see EPA mentioned in the same breath as DHA, especially on fish oil supplement labels. EPA (eicosapentaenoic acid) is the other main omega-3 fatty acid from marine sources. Both EPA and DHA often work together in the body, but they have their own specialties:
- EPA’s role: EPA is a 20-carbon fatty acid known mainly as an anti-inflammatory agent. It is the go-to omega-3 for producing signaling molecules (eicosanoids) that help calm inflammation. This makes EPA particularly beneficial for heart health (helping to keep blood vessels flexible and preventing clots) and for supporting a healthy inflammatory response in joints and throughout the body. EPA is also noted for its positive effect on mood – some research suggests that EPA-rich omega-3 supplements can help alleviate symptoms of depression and support emotional balance. In a nutshell, EPA is your “heart-healthy & inflammation-fighting” omega-3.
- DHA’s role: DHA, as we discussed, is a 22-carbon fatty acid that shines in brain, eye, and nervous system support. It is a structural component of cell membranes in the brain and retina. DHA is crucial for cognitive development and function at all ages, and is especially vital in pregnancy and infancy for building the brain architecture. It also helps maintain healthy blood pressure and has its own anti-inflammatory effects, but its starring role is being the “brain-building & vision-boosting” omega-3.
Think of EPA and DHA as complementary partners – a bit like a tag team. You will often find them together in fish oil because fish naturally provide both. Do you need both? Generally, yes. Most studies on omega-3 benefits have looked at combined intake of EPA and DHA. For overall adult health, having a mix of both is ideal: EPA keeps the cardiovascular system and inflammation in check, while DHA keeps the mind and eyes sharp.
That said, in specific situations one might be prioritised. For example, during pregnancy DHA is emphasised because of its direct role in fetal development (though EPA still plays a supportive part, such as aiding maternal mood and reducing inflammation). On the other hand, for someone looking to support mental health or lower triglycerides, a formula with more EPA might be suggested by healthcare providers.
Fortunately, you do not really have to choose one over the other in practice – many omega-3 supplements contain a balanced ratio. A standard fish oil capsule often contains roughly 180 mg EPA and 120 mg DHA per 1000 mg of oil (though concentrations vary). Some high-quality supplements are formulated to be “DHA-heavy” or “EPA-heavy” depending on the intended use. For instance, a prenatal DHA supplement might have a higher DHA:EPA ratio, whereas a cardiovascular-focused fish oil might have more EPA.
Bottom line: EPA and DHA are the dynamic duo of omega-3s. Each has unique benefits, but you need both for the full spectrum of omega-3 goodness. When you see “omega-3” on a supplement, it usually includes both EPA and DHA – the best of both worlds for your health.
Fish oil vs algae-based DHA: a vegan alternative
Traditional DHA supplements are derived from fish oil – typically from oily fish like anchovies, sardines, or tuna. But what if you follow a plant-based diet, have a fish allergy, or simply can’t stand the fishy aftertaste of some fish oils? Enter algae-based DHA supplements – the hero for vegetarians and vegans who need omega-3s.
Source difference: Fish do not actually produce DHA themselves; they get it by eating smaller marine organisms, like algae. By going straight to the source (microalgae), supplement manufacturers can produce DHA without involving fish at all. Algal oil is extracted from cultivated microscopic algae that are naturally rich in DHA. This makes algae oil 100% plant-based and vegan-friendly.
DHA content and EPA: One thing to note is that algae-based supplements often contain mostly DHA and little to no EPA (unless the product is fortified with additional EPA). Algal oil capsules commonly provide around 100–300 mg of DHA per serving. Some newer formulas are starting to include some EPA from algae as well, but in general, if you take algal DHA, you might not be getting much EPA. For most people, this is fine – your body can benefit greatly from the DHA, and a small amount of EPA can be converted from other omega-3s or obtained from your diet. If you specifically want EPA as a vegan, look for algae supplements that list EPA content or consider adding sources of ALA (which your body can partially convert to EPA).
Advantages of algae-based DHA: They are a great option for those who do not eat fish. Algal DHA supplements have no fishy smell or taste, and you will avoid the dreaded “fish burps” that some people experience with fish oil capsules. They are also considered environmentally sustainable – algae can be grown in labs or farms without depleting wild fish stocks, and production can be scaled without impacting ocean ecosystems. For the eco-conscious, this is a big plus. Additionally, because algae are grown in controlled conditions, the oil is naturally free from ocean contaminants like mercury or PCBs. In other words, purity is typically very high.
Fish oil advantages: This is not to say fish oil should be cast aside. Good quality fish oil is abundant, often more affordable per dose, and usually provides the benefit of both DHA and EPA together. Many fish oil supplements undergo molecular distillation or advanced purification to eliminate toxins, yielding a clean product. Fish oil has decades of research backing its benefits. If sustainability and dietary preferences allow, fish oil is an efficient way to get high doses of combined DHA and EPA.
To summarise the comparison:
- Fish Oil: Sourced from fish (not vegan); contains both DHA and EPA; typically more budget-friendly; widely available in various strengths; choose high-quality brands to ensure purity.
- Algae Oil: Sourced from microalgae (vegan-friendly); primarily DHA (EPA content may be minimal); no fishy taste; sustainable and pure; generally higher cost for the equivalent omega-3 yield.
Both sources can effectively raise your DHA levels and provide health benefits. In fact, studies have shown that algal DHA supplements are as effective as fish oil in increasing the body’s DHA status. So, if you are vegetarian or just prefer a plant-based option, you can take an algae-based DHA supplement with confidence that you are not missing out on the benefits.
Choosing a DHA supplement (dosage and tips)
When it comes to picking a DHA supplement, a few practical tips can help you make the best choice:
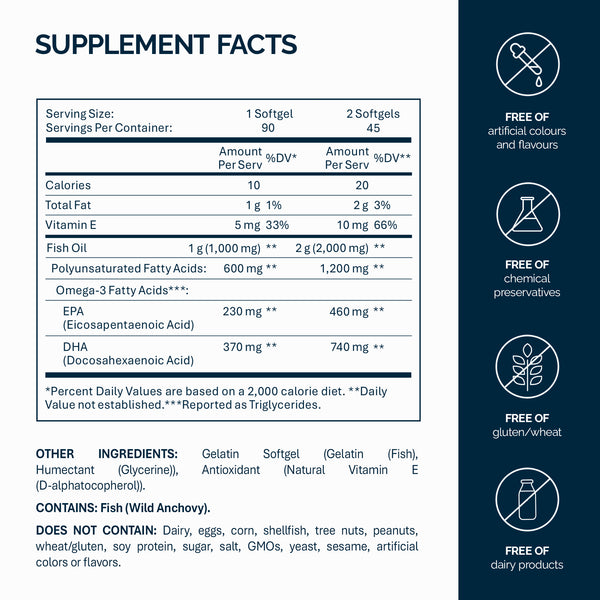
1. Check the DHA (and EPA) content: Look at the supplement facts label to see how much DHA and EPA are provided per serving. If you are pregnant or aiming for specific cognitive/vision benefits, you might prefer a formula higher in DHA. For general health or heart support, a balanced fish oil with both DHA and EPA is excellent. For example, NFO’s Omega-3 Strong DHA capsules provide 370 mg DHA and 230 mg EPA per capsule (740 mg DHA + 460 mg EPA in a two-capsule serving). This kind of high-DHA fish oil is ideal for meeting pregnancy needs or giving your brain an extra boost. On the other hand, a standard omega-3 capsule might have about 120 mg DHA and 180 mg EPA – you might need more capsules to reach the recommended intake. Know your goals and choose accordingly.
2. Quality and purity: Not all supplements are created equal. Opt for brands that are transparent about their sourcing and quality testing. Reputable omega-3 supplements will be purified to remove mercury, heavy metals, and other contaminants (especially crucial if you’re pregnant). Look for indications of third-party testing or quality seals (for instance, “IFOS certified” or standards met per pharmacopoeia guidelines). A high-quality product will ensure you get the benefits of DHA without any unwanted substances. If you’re considering fish oil, also check if the oil is in triglyceride form or ethyl ester form – triglyceride form is more natural and often better absorbed. If this detail is too technical, simply sticking to trusted brands or ones your healthcare provider recommends is a safe bet.
3. Sustainability and source: If environmental impact or vegetarian ingredients are important to you, lean towards algae-based DHA or fish oils certified by sustainability programs (like MSC or Friends of the Sea). Algal DHA is the go-to for vegans. If you choose fish oil, small fish (like anchovy or sardine oil) tend to be more sustainable and also lower on the food chain (hence lower in contaminants) compared to oil from large fish.
4. Dosage guidelines: For general adult maintenance of health, many experts suggest around 250–500 mg of combined DHA+EPA per day. This aligns with various guidelines for cardiovascular and overall health benefits. For pregnancy, as mentioned, at least 200–300 mg of DHA daily is recommended (often achieved with one high-strength capsule or two regular ones). Some prenatal supplements offer around 500–600 mg DHA to cover the needs in one go. It is usually safe (and often beneficial) to continue similar doses while breastfeeding, since DHA will enrich breast milk for the baby’s benefit. If you have specific health goals (like lowering triglycerides), doctors might recommend higher doses in the range of 1000–2000+ mg per day, but only take high doses under medical supervision.
5. How and when to take: DHA supplements are best absorbed when taken with food, especially a meal that contains some fat. So take your fish oil or algae oil capsule with breakfast or dinner rather than on an empty stomach. This can also help prevent any fishy aftertaste. Many prenatal DHA capsules are meant to be taken alongside your main prenatal vitamin (which is often with a meal anyway).
6. Medical advice and safety: As with any supplement, it is wise to consult your healthcare provider before starting, particularly if you are pregnant, breastfeeding, or have any medical conditions. DHA supplements are very safe for most people at moderate doses, but your doctor or midwife can give personalised guidance. They can confirm the appropriate dosage for your situation and check that it won’t interfere with any medications. For instance, omega-3s have a mild blood-thinning effect, which usually is not an issue at normal doses – in fact, it’s part of how they help the heart – but if you are on blood-thinner medication or have a bleeding disorder, your doctor should manage your intake. The good news is that national health agencies consider DHA and EPA supplements to be generally safe. Common minor side effects of fish oil can include a fishy aftertaste or mild digestive upset, but choosing enteric-coated or high-quality oil, and taking it with food, minimises this.
Lastly, remember that supplements are meant to supplement the diet, not replace healthy foods. Continue to eat omega-3 rich foods if you can (like fish, DHA-enriched eggs, or plant sources for ALA) alongside taking your supplement. And store your omega-3 capsules properly (in a cool, dry place, away from heat and light) to prevent them from going rancid.
Conclusion
DHA is a cornerstone of good health – from helping babies develop thriving brains and bright eyes, to keeping adults’ hearts, minds, and joints in top form. For expecting mums, DHA is a true champion nutrient, supporting a healthy pregnancy and setting the stage for baby’s future development. Compared to its partner EPA, DHA stands out for brain and vision benefits, while EPA brings its own strengths in heart health and inflammation relief – together, they are a powerful pair. Whether you get your omega-3s from fish oil or algae oil, the key is making sure you get enough of these beneficial fats in your routine.
When choosing a DHA supplement, consider your specific needs (pregnancy, general wellness, or dietary preferences) and pick a quality product you trust. A high-DHA fish oil like NFO Omega-3 Strong DHA is an excellent choice for those who want a potent dose of DHA and EPA from a reputable source. If you are vegan or simply prefer plant-based, an algae-derived DHA supplement will have you covered.
Incorporating DHA into your daily regimen is a simple step that can yield lifelong benefits, from supporting your ticker to nourishing your brain – and yes, even giving your future child the best start possible. Always keep it balanced and consult with a healthcare professional for personalised advice, especially during pregnancy. Here’s to enjoying the benefits of DHA and omega-3s as part of a healthy, vibrant lifestyle!
References:
- American Pregnancy Association – Omega-3 Fatty Acids: FAQs. (Discusses the importance of DHA and EPA during pregnancy, benefits for fetal development, and recommendations for intake.)
- Everlywell – EPA vs. DHA: Key differences explained. (Provides an overview of the distinct roles of EPA and DHA, including DHA’s critical role in brain/eye development and EPA’s anti-inflammatory benefits.)
- Verywell Health – Algae Oil vs Fish Oil: Which Omega-3 Source Is Better for Your Heart Health? (Covers the comparison between algal DHA supplements and fish oil, noting differences in omega-3 content, sustainability, and effectiveness. Includes dosage guidance and safety information.)
- National Institutes of Health (NIH) – Omega-3 Fatty Acids Fact Sheet for Health Professionals. (Highlights research findings such as DHA supplementation reducing risk of preterm birth, and provides official recommendations on omega-3 intake for various populations.)